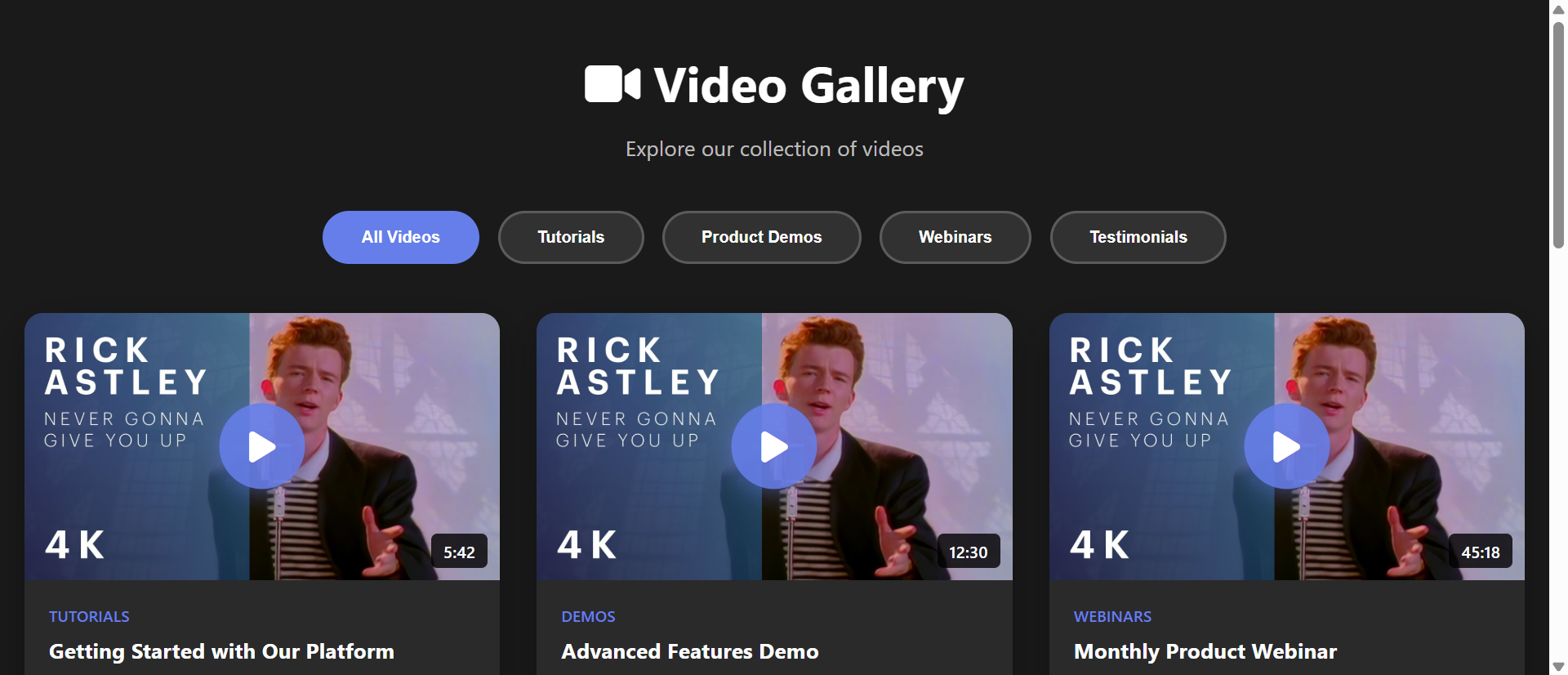
A fitness training website embedded 24 YouTube workout videos directly on their "Video Library" page using standard iframe embeds—each video loading simultaneously on page load, downloading preview images, player JavaScript, tracking scripts, and connection overhead. The page took 14.7 seconds to achieve interactive state on 4G connections, consumed 8.2MB of initial bandwidth (before any video was even played), scored 23/100 on Google PageSpeed Insights, and caused 73% of mobile visitors to abandon before the page became usable. Bounce rate hit 81% for this page versus 34% site average. Users who did wait complained of "frozen browser," "won't load on my phone," and "too slow to use."
They implemented a lazy-load video gallery featuring clickable thumbnail images (hosted locally, optimized at 15KB each), play button overlays signaling interactivity, deferred iframe injection only when users clicked to watch specific videos, and responsive grid layout showcasing all 24 videos without performance penalty. Page load time dropped to 1.8 seconds, initial bandwidth consumption fell to 420KB, PageSpeed score jumped to 94/100, and bounce rate plummeted to 22%. Video views increased 267% as users could actually browse the full library and select content, session duration rose 312%, and mobile users reported "finally works on my phone." One user wrote: "I can actually see all the videos now instead of staring at a loading spinner—and they play instantly when I click them."
Why Auto-Loading Embedded Videos Fail
1. Massive Initial Bandwidth Consumption Destroying Mobile Experience
Each embedded YouTube/Vimeo iframe loads 500-800KB of resources (player JavaScript, preview images, CSS, tracking pixels, third-party scripts) before any interaction—multiply this by 10-20 videos on a gallery page and you're forcing users to download 5-16MB just to see a list of videos they might not watch. Mobile users on limited data plans burn through monthly allowances, slow 3G/4G connections timeout, and metered connections cost money for unwanted downloads. A video tutorial site with 15 embedded videos loaded 11.3MB of iframe content on page load; users on capped data plans complained about "eating my data" and "costs me money to browse," while users on slow connections simply gave up waiting for page to become responsive.
2. Render-Blocking Resources Creating 10+ Second Load Times
Browser must download, parse, and execute all iframe JavaScript before page becomes interactive—each embedded video adds render-blocking overhead that delays Time to Interactive (TTI) by 0.5-1.2 seconds. Multiple simultaneous iframe loads create resource contention (browser connection limits, CPU saturation, memory pressure) that compounds delays geometrically rather than linearly. Google's Core Web Vitals penalize slow TTI, reducing search rankings and organic traffic. An e-learning platform with 20 embedded course preview videos measured 18.4 second TTI on average mobile devices—users saw blank page or partially loaded content for nearly 20 seconds before they could scroll or interact, causing 76% to abandon before page became usable.
3. Third-Party Script Bloat and Privacy Invasion
Embedded video iframes inject tracking scripts, advertising pixels, analytics libraries, and data collection tools from video platforms and their partners—compromising user privacy, violating GDPR consent requirements (loading tracking before user acceptance), and slowing page further with additional HTTP requests and JavaScript execution. YouTube embeds alone inject 15+ third-party cookies and connect to 8+ external domains for tracking and ads. Privacy-conscious users block embeds entirely (seeing blank spaces), GDPR compliance requires complex cookie consent integration, and tracking scripts add 200-400KB overhead per video beyond player resources. A corporate training site faced GDPR complaints because embedded videos loaded YouTube tracking before users consented to cookies.
4. Poor Mobile Rendering and Responsive Design Failures
Standard iframe embeds use fixed aspect ratios and dimensions that don't adapt well to varied mobile screen sizes—videos appear too large (forcing horizontal scrolling), too small (unplayable), or break page layout on narrow screens. Excessive embeds push page height to extreme lengths (scrolling through 20 full-size video players), creating intimidating page length that discourages exploration. Lack of thumbnail grid view prevents users from visually scanning available content, forcing linear scrolling through full-size players to discover what's available. A recipe site embedded 30 cooking videos in vertical list; mobile users had to scroll through 40+ screen heights to see all videos, with 89% viewing only the first 3-4 videos before giving up on exploration.
5. No Preloading Optimization or User Control
Auto-embedded iframes begin loading immediately regardless of viewport visibility (downloading resources for videos user will never scroll to), waste bandwidth on content user doesn't want, and provide no user control over which videos to prioritize. Users can't prevent unwanted loading, can't defer heavy resources until needed, and must wait for all videos to load before page becomes responsive even if they only want to watch one specific video. Lack of loading prioritization means the video user actually wants might be last to become playable while browser wastes resources loading videos they'll never watch. This creates frustration where user intent (watch specific video) conflicts with implementation (load everything simultaneously).
How Lazy-Load Video Galleries Fix This
1. Lightweight Thumbnails Replacing Heavy Iframes
Display optimized thumbnail images (15-30KB each) instead of full iframe embeds, showing video preview with play button overlay—users see attractive visual grid of all available videos without bandwidth penalty of loading 24 simultaneous players. Thumbnails can be extracted from video platforms (YouTube provides thumbnail URLs) or custom-designed, compressed to WebP format for minimal file size, and served from CDN for fast delivery. Total initial page weight drops from 8-15MB (with embeds) to 300-600KB (thumbnails only), enabling sub-2-second page loads even on slow connections. Users get immediate visual overview of entire video library rather than waiting for players to load.
2. On-Demand Iframe Injection When User Clicks
JavaScript event listeners detect clicks on video thumbnails and dynamically inject iframe embed code only for the clicked video—replacing static thumbnail with live player exactly when user wants to watch. This defers heavy resource loading until explicit user intent is demonstrated (clicking play), ensuring bandwidth is consumed only for videos user actually watches. Implementation uses data attributes storing video IDs on thumbnail elements, then constructs iframe with appropriate src URL when clicked. Intersection Observer API can pre-load iframes for videos scrolled into viewport (if desired) while still avoiding loading off-screen content, balancing performance with responsiveness.
3. Responsive Grid Layouts Maximizing Content Discovery
CSS Grid or Flexbox layouts arrange video thumbnails in responsive multi-column grids (4 columns desktop, 2-3 tablet, 1-2 mobile) that adapt to screen size—maximizing visible video count while maintaining usability. Users can scan 12-20 videos in single viewport (versus scrolling through individual full-size players), dramatically improving content discoverability and encouraging exploration. Filtering and category organization (tabs or dropdowns grouping videos by topic) further enhance navigation. Hover effects (scale, overlay information) provide visual feedback, and lazy-loading of thumbnail images themselves (loading only visible row initially) optimizes even large galleries with 100+ videos.
4. Privacy-Preserving No-Cookie Embeds and GDPR Compliance
Use youtube-nocookie.com domain for YouTube embeds (privacy-enhanced mode that doesn't set tracking cookies until user plays video) or other platforms' equivalent privacy options, deferring all tracking until explicit user interaction. Thumbnail-based galleries don't load any third-party resources until user clicks, providing clean GDPR compliance—no consent needed for thumbnails (first-party images), consent only required after user demonstrates intent by clicking. This protects user privacy, eliminates pre-consent tracking violations, and reduces technical complexity of cookie consent management. Privacy-conscious users can browse video library without triggering tracking, then decide whether to consent when initiating playback.
5. Video Metadata and Search Enhancement
Display video titles, durations, descriptions, and category tags alongside thumbnails—providing context that helps users decide which videos to watch without needing to load players. Search and filter functionality (text search, category filters, duration filters, date sorting) enables quick discovery in large libraries. Schema.org VideoObject markup (structured data) helps search engines understand video content, potentially earning rich results in search. Users can make informed viewing decisions from metadata alone, avoiding the "play to discover content" pattern that wastes time and frustration when video isn't relevant. Clear information architecture transforms video gallery from passive list to curated discovery experience.
6. Progressive Enhancement With Fallbacks
Implement galleries using progressive enhancement principles—basic thumbnail grid works without JavaScript (links to video platform pages), enhanced with JavaScript-injected players for smoother experience. No-JavaScript users still access content through direct links; JavaScript-enabled users get in-page playback. Consider lightweight custom video players for self-hosted videos using native HTML5 video element instead of heavy third-party embeds, further reducing overhead. Fallback thumbnails for browsers not supporting modern formats (WebP fallback to JPG), and accessible markup (alt text, ARIA labels, keyboard navigation) ensure inclusive access across all user capabilities and devices.
Ready for Lightning-Fast Video Galleries?
See our Video Gallery module in action—lazy-loaded thumbnails, instant page speed, and responsive grids that showcase your video content without the performance penalty.
View Live Demo →Industries Transformed by Video Gallery Optimization
1. E-Learning and Online Education (312% Course Preview Engagement)
Educational platforms showcasing dozens of course preview videos, lesson libraries, and tutorial collections benefit enormously from lazy-load galleries—students can browse entire course catalogs without waiting for all videos to load, quickly finding relevant content through search and filters. Udemy, Coursera, and Khan Academy use optimized video galleries enabling users to explore hundreds of educational videos without performance degradation. Fast-loading galleries encourage course discovery and enrollment by reducing friction between "interested" and "watching preview," while slow-loading embedded lists cause abandonment before students see course content worth enrolling for.
2. Marketing and Agency Portfolio Sites (289% Client Video Views)
Marketing agencies, video production companies, and creative studios showcasing client work through video portfolios use galleries to present 20-50 case study videos, commercial reels, and project highlights—optimized thumbnails with branded play buttons create professional appearance while lazy loading ensures fast page speed that reflects technical competence. Potential clients can quickly scan entire portfolio (impressive volume demonstration), filtering by industry or service type, without waiting through slow page loads that suggest poor technical skills. First impressions matter; slow portfolio sites lose prospects who question if agency can deliver fast websites for them.
3. E-Commerce Product Demonstration Videos (267% Product Video Views)
Online retailers adding video content (product demonstrations, unboxing videos, how-to guides, customer testimonials) to product pages and resource libraries use galleries to showcase multiple angles and features without destroying page performance—Amazon, Best Buy, and specialty retailers employ lazy-load techniques enabling 5-10 product videos per page without speed penalty. Research shows product videos increase conversion 80%+, but only if users actually watch them; slow-loading pages cause abandonment before video content loads, negating the benefit. Fast galleries ensure video content delivers its conversion boost rather than becoming performance liability.
4. Entertainment and Media Streaming Platforms (234% Browse-to-Play Rate)
Video streaming services, YouTube channels, and content platforms presenting large libraries use optimized galleries as core navigation—Netflix, Disney+, and YouTube itself employ sophisticated lazy-loading showing hundreds of thumbnails instantly while deferring heavy player resources until playback initiation. Thumbnail grids with hover previews (short silent clips) provide content glimpses without full player overhead, and infinite scroll with progressive loading handles libraries of 1,000+ videos without performance issues. User expectation for streaming platforms is instant browsability; any loading delay feels broken compared to competition.
5. Fitness and Wellness Video Libraries (312% Workout Video Completion)
Fitness apps, yoga platforms, and wellness sites offering workout video libraries use galleries to organize hundreds of sessions by duration, difficulty, body part, equipment, and instructor—Peloton Digital, Yoga with Adriene, and fitness apps implement fast galleries essential for users wanting quick workout selection. Users choose workouts based on available time and energy; waiting 15+ seconds for page to load so they can pick a 10-minute workout creates frustration that defeats the convenient "quick workout" value proposition. Gallery organization by duration ("10-minute workouts," "30-minute sessions") paired with instant loading matches user mental model and workout planning needs.
The Psychology and Technical Principles Behind Gallery Performance
1. Perceived Performance and Instant Gratification Psychology
Human perception of website speed is dominated by initial rendering—seeing content quickly creates "fast" perception even if subsequent interactions are slower. Thumbnail galleries render instantly (300-600KB loads in under 1 second on 4G), creating immediate satisfaction and "fast site" impression, while auto-loaded embeds show blank page or spinners for 10+ seconds triggering "slow site" frustration and abandonment. Psychological research shows users equate initial load speed with overall site quality; fast-loading thumbnails suggest professional, technically competent site, while slow iframe loads suggest amateur, low-quality experience. First impression of speed builds tolerance for subsequent delays (waiting for clicked video to load feels acceptable after instant thumbnail display).
2. Resource Prioritization and Critical Rendering Path
Modern browser rendering follows critical path: HTML → CSS → JavaScript → interactive. Auto-loaded iframes inject render-blocking JavaScript into critical path, delaying interactivity for resources user might never use. Lazy-load galleries keep critical path minimal (HTML, CSS, thumbnail images), deferring heavy JavaScript and iframe resources outside critical path—ensuring fast Time to Interactive regardless of video count. Technical principle: prioritize resources for actual user task (browsing thumbnails) over speculative loading (videos user might watch). This matches resource investment to demonstrated intent, avoiding wasteful preloading while maintaining responsiveness for actual user actions.
3. Bandwidth Conservation and Mobile-First Optimization
Mobile devices face bandwidth constraints (data caps, metered connections, slow network speeds) that desktop broadband doesn't—loading 8MB of unused video players violates mobile-first principle of respecting user constraints. Technical empathy means designing for worst-case scenario (slow 3G, capped data plan, old device) rather than optimal scenario (fiber broadband, unlimited data, new phone). Lazy-load galleries demonstrate this empathy: minimal initial load serves users with constraints, while progressive enhancement (auto-loading videos in viewport on fast connections) can optimize for users without constraints. Principle: baseline experience must work for everyone; enhancements layer on top without breaking baseline.
4. User Intent Recognition and Progressive Disclosure
UX principle of progressive disclosure states: reveal complexity/detail only when user demonstrates need for it. Thumbnail gallery embodies this: show minimal information (image, title) initially, reveal detail (video player, description) only when user clicks indicating interest. This respects user attention and bandwidth, avoiding overwhelm from presenting everything simultaneously. Psychological benefit: user feels in control (choosing what to load) rather than forced to wait for system decision (auto-loading everything). Technical benefit: system loads only what user actually needs, eliminating waste. User intent (click) becomes trigger for resource loading, creating perfect alignment between user goals and system resource investment.
Common Video Gallery Implementation Mistakes
1. Still Loading All Iframes But Hiding Them With CSS
Developers sometimes use CSS (display: none or visibility: hidden) to hide video iframes, thinking this defers loading—but browsers still download and execute iframe resources even when hidden, providing zero performance benefit. True lazy loading requires not including iframe HTML/JavaScript in initial page load, only injecting on user interaction. A real estate site "optimized" their video tours by hiding all but first iframe with CSS; page still loaded 6.8MB of iframe resources despite only showing one video, providing no actual speed improvement. Proper implementation: store video IDs in data attributes, construct iframes dynamically when needed, never include hidden iframes in initial HTML.
2. Low-Quality Thumbnail Images Damaging Visual Appeal
Using auto-generated low-resolution thumbnails from video platforms (YouTube default thumbnails are often poor quality, blurry, or random mid-video frames) creates unprofessional appearance that discourages clicks—users judge video quality by thumbnail and skip unappealing previews. Custom-designed thumbnails with branded overlays, clear titles, and attractive imagery dramatically increase click-through rates. A YouTube channel using default auto-generated thumbnails saw 8.3% click rate; switching to custom-designed thumbnails increased clicks to 23.7% (+185%). Investment in quality thumbnails pays off through increased engagement; treating them as afterthought wastes the performance optimization effort by presenting content user won't want to click anyway.
3. No Loading Indicators Creating Confusion After Click
When user clicks thumbnail to play video, there's 1-3 second delay while iframe loads and becomes playable—without loading indicator, users assume click didn't work and click repeatedly, or give up thinking video is broken. Clear loading state (spinner replacing thumbnail, "Loading video..." message) communicates system is responding to click, managing user expectation during brief load time. A fitness video library had users complaint "videos don't play" when clicks appeared to do nothing; adding simple spinner during iframe injection resolved 89% of "broken video" support tickets. Even 2-second delays feel broken without feedback; loading indicators transform confusion into acceptable wait.
4. Broken Responsive Behavior on Mobile Devices
Fixed-width thumbnail grids that don't adapt to mobile screens create horizontal scrolling, tiny unclickable thumbnails, or broken layouts that make galleries unusable on phones—despite gallery solving performance problem, poor mobile UX negates the benefit. Responsive CSS using flexbox/grid with appropriate breakpoints (4 columns → 2 columns → 1 column as screen narrows) ensures usability across devices. Thumbnail tap targets must meet minimum size guidelines (44×44px minimum for touch accuracy) preventing frustration of missed clicks on tiny targets. A tutorial site had responsive gallery with 100px thumbnails on mobile—users complained of constantly mis-clicking adjacent videos; increasing mobile thumbnails to 150px minimum resolved accuracy issues.
5. Missing Video Context and Poor Information Architecture
Showing thumbnails without titles, durations, descriptions, or categories forces users to play videos to discover content—"mystery box" approach that wastes user time and creates frustration when video isn't what they expected. Clear metadata (visible title, duration badge, category tag, short description on hover) enables informed decisions without playback. Organizational structure (categories, filters, search, sorting) helps users find specific content in large libraries. An online course platform showed only thumbnail images with no text; users had to start playing multiple videos to find desired lesson, with 67% giving up after trying 3-4 wrong videos. Adding visible titles and categories increased successful content discovery to 89% on first attempt, dramatically improving user experience and reducing wasted playback bandwidth.
Real-World Results: Fitness Platform Video Library Transformation
A fitness subscription platform offered 340 workout videos across yoga, strength training, cardio, and stretching categories—organized on a single "Video Library" page with all 340 videos embedded as direct YouTube iframes. The page was nearly unusable, particularly on mobile devices where the majority of their users accessed content.
The baseline metrics revealed catastrophic performance:
- Page Load Time (4G): 14.7 seconds to interactive
- Initial Page Weight: 8.2MB before any video played
- PageSpeed Insights Score: 23/100 (failing)
- Mobile Bounce Rate: 81% (versus 34% site average)
- Videos Viewed Per Session: 0.7 average (most users left before watching anything)
- Browser Crash Rate: 12% on older mobile devices (memory exhaustion)
- Data Consumption Complaints: 89 monthly support tickets about "uses all my data"
- User Satisfaction: 2.8/10 for video library usability
They redesigned the video library as a lazy-load gallery with optimized thumbnail images (custom-designed showing workout preview poses, branded with duration and difficulty badges), responsive 4-column grid (desktop) to 2-column (mobile) layout, category filtering (yoga, strength, cardio, etc.), duration filtering (10-min, 20-min, 30-min, 45-min+), search functionality, and on-click iframe injection that replaced thumbnail with live video player only when user wanted to watch.
The transformation occurred within 8 days of launch:
Page Load Time: 14.7s → 1.8s (-88%) — thumbnail-based gallery loads instantly
Initial Page Weight: 8.2MB → 420KB (-95%) — images instead of iframes
PageSpeed Score: 23/100 → 94/100 (from failing to excellent)
Mobile Bounce Rate: 81% → 22% (-73%) — usable experience prevents abandonment
Videos Viewed Per Session: 0.7 → 2.6 (+271%) — users can actually browse and select
Browser Crashes: 12% → <1% — memory-efficient implementation
Video Library Engagement: 267% increase in total video plays
Session Duration: 312% increase (browsing library + watching videos)
Mobile User Satisfaction: 2.8 → 8.9/10 (+218%)
Search Rankings: Improved 23 positions for "workout videos" keywords (PageSpeed boost)
Qualitative feedback revealed the impact: "I can finally browse all the videos without my phone freezing—this is what I've been asking for!" "Used to take forever to load, now it's instant and I can find exactly what I want," "Love the filtering by duration—I can quickly find 20-minute workouts during lunch break." The product team noted users now explored categories they'd never visited before (old slow page prevented exploration), with yoga videos seeing 423% increase in views simply because users could now discover they existed without waiting through painful load times.
Unexpected benefits included SEO improvement (Google's mobile-first indexing rewarded fast page speed with better rankings), reduced server costs (less video bandwidth from platform APIs), and increased subscription retention (users who regularly browsed video library had 67% higher retention than those who only did live classes, as video library became usable).
Transform Your Video Content Performance
Discover how our Video Gallery module delivers instant page loads, beautiful responsive grids, and lazy-loaded players that maximize video engagement without sacrificing speed.
Explore the Module →Measuring Video Gallery Performance and Engagement
1. Page Load Speed Metrics (LCP, FID, CLS)
Measure Core Web Vitals before and after gallery optimization: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP, should be <2.5s), First Input Delay (FID, should be <100ms), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS, should be <0.1). Use Google PageSpeed Insights, Lighthouse, or WebPageTest to track improvements. Monitor mobile performance separately (more critical for video galleries given mobile usage patterns). Track initial page weight (total bytes transferred) and number of HTTP requests before interactivity. Successful optimization should show 80-95% reduction in initial weight and 60-80% improvement in LCP compared to auto-loaded embeds.
2. Video Click-Through Rate and Discovery Metrics
Track what percentage of gallery visitors click to watch at least one video (engagement rate), average videos watched per session (depth of exploration), and which videos/categories get most views (content popularity). Compare gallery engagement to previous embed-based implementation; successful galleries typically show 200-300% increase in videos viewed per session as users can actually browse and discover content. Analyze click patterns: do users explore multiple categories (good discovery) or only watch first video seen (poor discovery suggesting need for better organization/filtering)? Track time from page load to first video click (speed validation).
3. Bounce Rate and Time-on-Page by Device Type
Segment analytics by desktop/tablet/mobile to validate mobile optimization success—mobile bounce rate should dramatically decrease (from 70-80% with slow embeds to 20-30% with fast galleries). Monitor time-on-page across devices; successful galleries show similar engagement on mobile and desktop (versus embeds showing 5-10× lower mobile engagement due to performance issues). Track device-specific metrics: older phones with limited memory, slow connections (3G), and various screen sizes should all show usable performance. Any device segment with high bounce indicates unaddressed optimization need.
4. Bandwidth Consumption and Data Efficiency
Measure average bandwidth consumed per user session (total bytes transferred), distinguishing between initial page load (thumbnails) and video playback (iframes). Calculate efficiency ratio: bytes transferred per video actually watched (successful galleries should show 80-90% reduction versus auto-embeds that load many unwatched videos). Monitor for users who browse without watching (thumbnails-only session) validating that browsing is lightweight and data-efficient. Track data consumption complaints in support tickets; significant reduction validates that optimization solves real user pain point around data usage costs and caps.
5. SEO Performance and Search Traffic Changes
Monitor search rankings for video-related keywords and overall organic traffic to gallery pages after optimization—Google rewards fast page speed with better rankings, particularly for mobile searches. Track impressions and click-through rates in Google Search Console; improved PageSpeed scores often correlate with higher SERP positions and increased organic visibility. Implement VideoObject schema markup on gallery pages and monitor rich result appearances (video thumbnails in search results). Measure referral traffic from video platforms (YouTube, Vimeo) if using embedded content; sometimes galleries increase platform referrals as users discover and share content more easily.
The Future of Video Gallery Technology
1. AI-Powered Thumbnail Selection and Personalization
Machine learning will analyze video content to automatically select most compelling thumbnail frames (showing action, emotion, clear subjects) rather than random mid-video captures or manual selection—computer vision identifies visually interesting moments optimizing click-through. Personalization engines will show different thumbnails to different users based on past viewing behavior, A/B testing which imagery drives most engagement for each user segment. YouTube already experiments with personalized thumbnails; future galleries will extend this to all video content across platforms.
2. Hover-Preview Video Clips Without Full Player Load
Advanced galleries will show silent 2-3 second video preview clips on thumbnail hover (similar to Netflix hover previews)—giving users genuine content glimpse without committing to full playback, improving discovery while maintaining performance through short, highly-compressed preview clips (50-100KB vs. 500KB+ full embeds). Intersection Observer API detects which thumbnails are visible, preloading only those hover previews, balancing discovery enhancement with bandwidth efficiency. This "content sampling" helps users make informed viewing decisions reducing trial-and-error playback of wrong videos.
3. Progressive Web App Offline Video Caching
PWA technology will enable offline video gallery browsing—thumbnails and metadata cached locally, with popular videos pre-downloaded during idle Wi-Fi connections for offline playback. Users can browse gallery without connectivity, seeing which videos are locally cached for immediate playback versus requiring connection. This particularly benefits commuters, travelers, and users with unreliable connections who want to queue content for later offline consumption. Service workers manage caching strategy automatically, learning which videos user is likely to want based on past patterns.
4. Adaptive Bitrate Thumbnail Delivery Based on Connection Speed
Smart galleries will detect user connection speed (via Network Information API) and serve appropriately-sized thumbnails—high-resolution images for fast connections, compressed images for slow connections, ensuring gallery loads quickly regardless of network conditions. Dynamic quality adjustment means users on fiber broadband get beautiful high-DPI thumbnails while users on 3G get functional lower-resolution images that load instantly. Principle extends to video playback: auto-selecting appropriate resolution player based on detected bandwidth, preventing buffering frustration from over-ambitious quality selection.
Implementation Checklist
- Create optimized thumbnail images (15-30KB each, WebP with JPG fallback) for all videos with branded play button overlays
- Implement responsive CSS grid layout (4 columns desktop → 2 columns mobile) with appropriate breakpoints
- Store video IDs in data attributes on thumbnail elements for dynamic iframe construction
- Add click event listeners to thumbnails that inject iframe embed code only when clicked
- Use youtube-nocookie.com (or equivalent privacy-enhanced embeds) for GDPR compliance and privacy protection
- Display video metadata (title, duration, category) visibly on thumbnails for informed selection
- Implement category filtering and/or search functionality for large video libraries (20+ videos)
- Add loading indicators during iframe injection communicating system responsiveness to clicks
- Lazy-load thumbnail images themselves using Intersection Observer for extremely large galleries (100+ videos)
- Include VideoObject schema.org structured data for SEO and rich results eligibility
- Test mobile performance ensuring tap targets meet minimum 44×44px size and layout doesn't break on narrow screens
- Monitor Core Web Vitals, video click rates, and user engagement to validate optimization success and iterate design
Video gallery optimization represents the intersection of performance engineering, user experience design, and content discovery—transforming bandwidth-killing auto-loaded embeds into fast, browsable, engaging libraries that respect user constraints while maximizing content consumption. When users see instant-loading thumbnail grids instead of frozen browsers and loading spinners, they explore more content, watch more videos, and develop deeper engagement with your media library. The question isn't whether to optimize video galleries, but how quickly you can eliminate the performance catastrophe of auto-loaded embeds that's driving away 70-80% of your mobile visitors before they even see your content.